PMP Exam Pattern
1. Question Types in PMP Exam
The PMP exam includes a variety of question formats to test both knowledge and application skills:
Multiple-choice (Single Answer) – one correct option.
Multiple Responses – choose all options that apply.
Matching – pair terms with the correct definitions, tools, or processes.
Fill-in-the-blank – type a numeric or short text answer.
Hotspot – identify or select the correct area on an image or diagram.
2. Question Distribution by Domains
Based on PMI’s current Exam Content Outline (ECO), PMP exam questions are distributed across three domains:
People – 42% (leadership, team performance, communication, stakeholder engagement).
Process – 50% (technical project management, planning, scheduling, risk, and execution).
Business Environment – 8% (compliance, value delivery, organizational alignment, strategy).
3. Question Difficulty & Style
The PMP exam is designed to assess real-world project management expertise with a mix of question styles:
Situational Questions (70–80%) – scenario-based, requiring you to apply judgment.
Example: “You are managing a project and a key stakeholder disagrees with the project approach. What should you do first?”
Knowledge-based Questions – test definitions, processes, and framework understanding.
Application-based Questions – ask you to apply PM principles in real-life project situations, often blending Agile, hybrid, and predictive methods.
4. Question Sources
PMP exam questions are derived from multiple references that reflect both predictive and agile approaches:
PMBOK® Guide (latest edition) – predictive project management processes and tools.
Agile Practice Guide – agile and hybrid methodologies.
Industry Best Practices & PMI Code of Ethics – professional conduct and practical standards applied globally.
PMP Exam Questions
People (42%)
Leadership, communication, stakeholder management, and team performance.
1. A team member frequently misses deadlines. As a project manager, what should you do first?
Escalate to the sponsor
Address the issue privately with the team member
Reassign the tasks
Document the issue in lessons learned
Answer: 2
Explanation: Addressing issues privately encourages open dialogue, helps identify root causes, and avoids unnecessary escalation that could harm morale.
2. A stakeholder is unhappy with project progress. How should you handle the situation?
Ignore concerns until delivery
Schedule a meeting to understand their expectations
Ask the sponsor to intervene
Add more resources without approval
Answer: 2
Explanation: Directly engaging stakeholders through meetings clarifies concerns and builds trust, ensuring alignment with project goals.
3. You notice conflict between two team members during a sprint. What is your best response?
Replace one team member
Facilitate a discussion to resolve the conflict
Escalate to HR immediately
Ignore unless it impacts work
Answer: 2
Explanation: The project manager should act as a mediator, facilitating constructive discussions to resolve conflicts and preserve teamwork.
4. A new team member joins mid-project. What is the most important first step?
Assign tasks right away
Introduce them to stakeholders
Provide project onboarding and explain roles/responsibilities
Ask them to shadow another team member
Answer: 3
Explanation: Proper onboarding ensures the team member understands context, responsibilities, and processes, leading to faster integration.
5. During a team retrospective, members hesitate to share issues. What should you do?
Skip the session
Encourage open discussion by setting a safe environment
Report non-participation to HR
Extend the project schedule
Answer: 2
Explanation: Creating a psychologically safe environment allows honest sharing, which is key to continuous improvement.
6. Which leadership style is most effective in Agile environments?
Autocratic
Servant leadership
Directive
Transactional
Answer: 2
Explanation: Servant leadership empowers teams, removes obstacles, and fosters collaboration, aligning perfectly with Agile principles.
7. A senior stakeholder asks for a major scope change without following change control. How should you respond?
Accept the request to maintain stakeholder satisfaction
Add it to the backlog and review formally
Escalate immediately to the sponsor
Reject the change without explanation
Answer: 2
Explanation: All scope changes must go through the formal change control process to maintain project stability.
8. When coaching underperforming team members, the project manager should:
Provide constructive feedback and mentoring
Reduce their workload permanently
Publicly address performance gaps
Request a replacement from HR
Answer: 1
Explanation: Coaching builds capability while maintaining respect and morale, instead of reducing workload or replacing members prematurely.
9. Your distributed team struggles with miscommunication due to time zones. What’s the best action?
Reduce meetings altogether
Implement overlapping work hours and better collaboration tools
Assign all communication to one lead
Extend project deadlines
Answer: 2
Explanation: Overlapping hours and effective tools enhance collaboration, reducing miscommunication across distributed teams.
10. The best way to engage resistant stakeholders is to:
Exclude them from meetings
Understand their concerns and address them proactively
Ask the sponsor to replace them
Escalate every issue
Answer: 2
Explanation: Actively listening and addressing concerns helps reduce resistance, strengthening stakeholder engagement.
11. A sponsor insists on micromanaging your team. How should you handle it?
Allow it since they are funding the project
Clarify governance roles and responsibilities with the sponsor
Escalate to the steering committee
Reduce stakeholder involvement
Answer: 2
Explanation: Clarifying roles ensures governance balance, preserving team autonomy and productivity.
12. A project manager wants to motivate a cross-functional team. Which method is most effective?
Extrinsic rewards only
Recognition, empowerment, and growth opportunities
Strict performance monitoring
Limiting communication
Answer: 2
Explanation: Recognition and empowerment foster intrinsic motivation, which sustains team performance long-term.
Process (50%)
Technical project management, planning, scheduling, risk, and execution.
13. What is the primary purpose of a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)?
Sequence project activities
Define deliverables and project scope
Estimate costs
Track risks
Answer: 2
Explanation: WBS decomposes deliverables into smaller tasks, clearly defining project scope.
14. A project is behind schedule. What tool should you use to determine the impact?
Monte Carlo simulation
Critical Path Method (CPM)
Earned Value Management (EVM)
Ishikawa diagram
Answer: 2
Explanation: CPM identifies task dependencies and reveals delays affecting project duration.
15. During risk planning, you identify a risk with high probability and high impact. What’s the best response?
Accept it
Mitigate it
Transfer it
Avoid it
Answer: 2
Explanation: Mitigation reduces the likelihood or impact of high-priority risks proactively.
16. The cost performance index (CPI) is 0.8. What does this indicate?
Project is under budget
Project is over budget
Project is ahead of schedule
Project is on track
Answer: 2
Explanation: CPI < 1 means the project is overspending compared to planned cost efficiency.
17. What is the best method for estimating project costs when historical data is available?
Parametric estimation
Bottom-up estimation
Three-point estimation
Reserve analysis
Answer: 1
Explanation: Parametric estimation uses data-driven models, providing reliable estimates from past data.
18. A project sponsor asks for a completion date earlier than planned. What should you do?
Crash or fast-track the schedule after analyzing trade-offs
Agree immediately
Add unapproved resources
Ignore the request
Answer: 1
Explanation: Crashing and fast-tracking are valid methods to shorten schedules without scope changes.
19. A defect is found after product delivery. Which process was likely inadequate?
Quality planning
Scope management
Risk analysis
Communications management
Answer: 1
Explanation: Proper quality planning ensures preventive measures to minimize post-delivery defects.
20. What tool is best for identifying root causes of quality issues?
Pareto chart
Fishbone diagram
Gantt chart
Control chart
Answer: 2
Explanation: Fishbone diagrams identify possible root causes systematically for quality issues.
21. What does SPI < 1 indicate in Earned Value Management?
Ahead of schedule
Behind schedule
On track
Over budget
Answer: 2
Explanation: SPI < 1 signals project work is progressing slower than planned.
22. A vendor fails to deliver on time. Which document governs the response?
Procurement statement of work
Risk register
Contract agreement
Change request form
Answer: 3
Explanation: Contracts are binding documents that define remedies for vendor failures.
23. Which scheduling method emphasizes resource limitations?
Critical Path Method
Resource leveling
Fast-tracking
Crashing
Answer: 2
Explanation: Resource leveling adjusts schedules to fit within resource limits, often extending duration.
24. Which Agile tool is used to visualize workflow and WIP limits?
Gantt chart
Burndown chart
Kanban board
Pareto chart
Answer: 3
Explanation: Kanban boards make workflows visible and track WIP limits for efficiency.
25. A project manager wants to forecast the final project cost. Which metric should be used?
ETC
EAC
VAC
CV
Answer: 2
Explanation: Estimate at Completion forecasts final project cost, incorporating performance trends.
26. Which process involves ensuring deliverables are formally accepted?
Control Quality
Validate Scope
Define Scope
Monitor Risks
Answer: 2
Explanation: Validate Scope is the process where deliverables are formally reviewed and accepted by stakeholders, confirming requirements are met.
27. Which Agile event ensures team alignment on work for the iteration?
Sprint Review
Sprint Planning
Daily Stand-up
Retrospective
Answer: 2
Explanation: Sprint Planning aligns the Agile team on the backlog items for the sprint and sets iteration goals collaboratively.
28. Which contract type carries the most risk for the buyer?
Cost Plus Award Fee
Firm Fixed Price
Time and Material
Fixed Price Incentive Fee
Answer: 3
Explanation: Time and Material contracts expose the buyer to greater cost risk since duration and resource use are uncertain.
29. Which is the best way to prioritize risks?
Risk register only
Probability and impact matrix
Lessons learned
Brainstorming
Answer: 2
Explanation: A probability-impact matrix quantifies risks by likelihood and effect, providing a clear prioritization method.
30. A project has CPI = 1.2 and SPI = 0.9. What does this mean?
Under budget, ahead of schedule
Over budget, behind schedule
Under budget, behind schedule
Over budget, ahead of schedule
Answer: 3
Explanation: CPI > 1 shows cost efficiency (under budget), while SPI < 1 shows delays (behind schedule).
31. Which document formally authorizes a project?
Project Charter
Statement of Work
Business Case
Scope Statement
Answer: 1
Explanation: The Project Charter is the official document that authorizes a project and grants the project manager authority.
32. Which technique is best for determining stakeholder influence and interest?
RACI matrix
Stakeholder engagement matrix
Pareto chart
Communication plan
Answer: 2
Explanation: The stakeholder engagement matrix maps influence vs. interest, helping project managers plan engagement strategies.
33. Which approach helps in analyzing uncertainty in project schedule?
Monte Carlo simulation
Earned Value Management
Fast-tracking
Delphi technique
Answer: 1
Explanation: Monte Carlo simulation models multiple scenarios to assess uncertainties and predict outcomes.
34. A project team delivers features iteratively with stakeholder feedback every 2 weeks. Which approach are they using?
Waterfall
Agile
Critical Path Method
Parametric Estimation
Answer: 2
Explanation: Agile emphasizes iterative delivery and frequent stakeholder feedback for continuous improvement.
35. Which document defines how risks will be identified, analyzed, and managed?
Risk Management Plan
Risk Register
Scope Baseline
Communications Plan
Answer: 1
Explanation: The Risk Management Plan describes the framework and methodology for handling project risks.
36. Which metric shows cost variance?
CPI
SPI
CV
EV
Answer: 3
Explanation: Cost Variance (CV = EV – AC) measures how much the project is under or over budget.
37. In Agile, velocity is used for:
Tracking costs
Measuring stakeholder satisfaction
Estimating team capacity for future sprints
Assigning resources
Answer: 3
Explanation: Velocity is a planning tool in Agile, used to forecast how much work a team can complete in future sprints.
38. The project manager needs to manage stakeholder expectations. Which document helps most?
Stakeholder engagement plan
Work Breakdown Structure
Lessons learned
Network diagram
Answer: 1
Explanation: The stakeholder engagement plan outlines strategies and communication methods for managing expectations effectively.
Business Environment (8%)
Compliance, strategic alignment, and value delivery.
39. A project must comply with new government regulations. What should you do first?
Stop project execution until clarified
Review how compliance impacts project scope and costs
Escalate to stakeholders only
Ignore until an audit occurs
Answer: 2
Explanation: The first step is to assess how compliance impacts project scope, cost, and schedule before taking corrective action.
40. A project is not aligned with organizational strategy. What’s the best action?
Continue as planned
Recommend termination to leadership
Ignore misalignment
Add extra resources
Answer: 2
Explanation: Projects that do not support organizational strategy waste resources; recommending termination is best practice.
41. A new CEO changes the company’s strategic priorities. How should the project manager respond?
Review project alignment with new goals
Continue as-is until project closure
Request additional budget
Replace team members
Answer: 1
Explanation: Reviewing alignment ensures the project still supports organizational objectives under new leadership.
42. Value delivery in projects is best measured by:
Earned Value
Business outcomes achieved
Budget adherence only
Stakeholder satisfaction only
Answer: 2
Explanation: The real measure of project success is delivering tangible business outcomes, not just outputs.
43. Which document defines how the project benefits will be measured after delivery?
Benefits Management Plan
Scope Statement
Stakeholder Register
Charter
Answer: 1
Explanation: The Benefits Management Plan ensures benefits are defined, tracked, and realized after project completion.
44. Which best describes “tailoring” in project management?
Adjusting processes to fit project context
Customizing stakeholder expectations
Modifying PMBOK permanently
Skipping required processes
Answer: 1
Explanation: Tailoring means adapting project management processes to the specific needs of a project.
45. Compliance issues discovered late in execution usually mean:
Inadequate monitoring of external environment
Improper budgeting
Overstaffing
Ineffective Agile practices
Answer: 1
Explanation: Late discovery of compliance gaps indicates insufficient monitoring of external legal and regulatory changes.
46. Which approach ensures continuous alignment with business objectives?
Earned Value Management
Benefits realization management
Stakeholder analysis
Critical Path Method
Answer: 2
Explanation: Benefits realization management ensures delivered outcomes match intended business objectives.
47. Which organization publishes the PMP exam?
Scrum.org
Project Management Institute (PMI)
AXELOS
PRINCE2 Foundation
Answer: 2
Explanation: PMI (Project Management Institute) is the official body that develops and administers the PMP exam.
48. A project delivers on time and on budget, but customers are dissatisfied. Which aspect failed?
Value delivery
Scheduling
Procurement
Team performance
Answer: 1
Explanation: Even if cost and schedule are met, poor value delivery means project failure from a customer perspective.
49. Which environmental factor can most influence project compliance?
Legal and regulatory requirements
Organizational hierarchy
Team culture
Lessons learned
Answer: 1
Explanation: Legal and regulatory requirements drive compliance, making them the most influential environmental factor.
50. Which framework ensures project outcomes align with organizational goals?
PMBOK Guide
Portfolio Management
Risk Register
Network Diagram
Answer: 2
Explanation: Portfolio Management ensures that all projects and programs contribute to strategic alignment and value delivery.
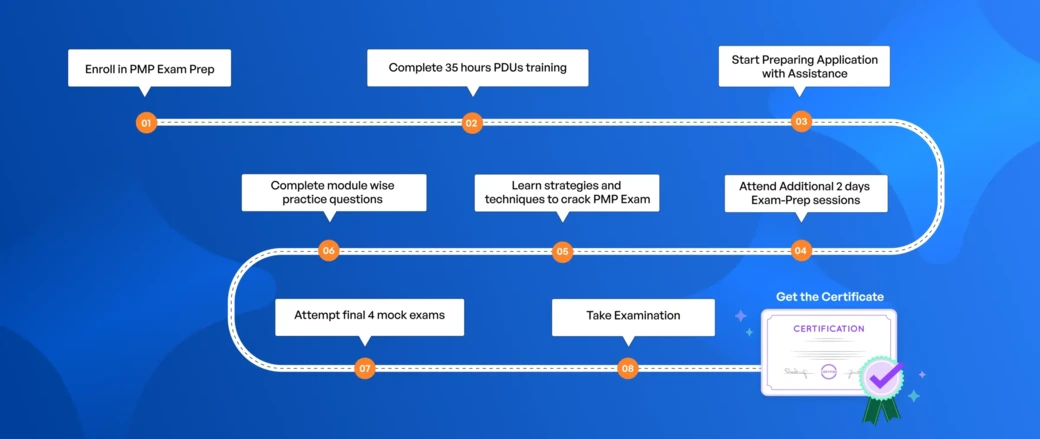
Recommended Question Practice Strategy
Preparing for the PMP exam isn’t just about studying concepts — it’s about building the ability to apply knowledge in real-world scenarios. Here’s a step-by-step practice strategy:
Start with Domain-Focused Practice and enhance your preparation with AI PMP prep to gain deeper insights and practical understanding.
Break your preparation into People (42%), Process (50%), and Business Environment (8%) domains.
Attempt at least 20–30 questions per domain to identify your weak areas.
Prioritize Situational Questions
Around 70–80% of the PMP exam questions are scenario-based.
Focus on questions that ask “What should you do first?” — they test application, judgment, and PMI’s mindset.
Mix Question Types
Practice across multiple-choice, multiple-response, matching, fill-in-the-blank, and hotspot questions.
This will help you get comfortable with PMI’s exam format.
Simulate Exam Conditions
Attempt full-length mock exams (180 questions, 230 minutes) to build stamina.
Avoid checking answers until the test is complete to mirror real exam pressure.
Review Explanations Thoroughly
Don’t just note correct answers — analyze why other options are incorrect.
Focus on PMI’s perspective of best practices (e.g., stakeholder engagement before escalation).
Track Your Progress
Keep a log of incorrect answers.
Revisit weak areas weekly and align them with PMBOK® Guide and Agile Practice Guide.
Balance Predictive, Agile, and Hybrid
PMP integrates predictive (waterfall), agile, and hybrid practices.
Ensure you practice questions across all three approaches.
Final Revision Phase
In the last 2 weeks, focus on timed mock tests and quick review notes.
Prioritize high-weightage topics: risk, stakeholder engagement, scheduling, and agile practices.