What is Software Testing?
Software testing is a systematic process that involves evaluating and validating a software application to identify defects, errors, and discrepancies. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including test planning, test case design, execution, and defect reporting. A qualified software tester plays a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity and performance of software products before they are released to end-users.
Also Read: Software Testing Life Cycle
Who is a Software Tester?
A software tester is someone who uses their skills to guarantee that computer programs or software perform as intended. They must ensure that the program runs well and that there are no issues in the final result. This also aids in discovering any flaws in the product and correcting them before the final product is manufactured. This will allow enterprises to deliver the products their customers require.
Also Read: Quality Assurance Vs Quality Control
What does a Software Tester do?
A software tester's responsibility varies depending on the firm, but essentially he or she studies the software and discovers defects, eliminating poor performance and interface difficulties. They must also conduct several tests at various stages of the software development life cycle. Let us look at the fundamental duties of a software tester:
- They must gather and document manual and automated testing.
- They must carry out tests, examine the data, and report on anything that needs to be improved or corrected.
- They must test in all phases, including design, development, testing, release, and maintenance.
- System requirements must be examined.
- Report any concerns discovered during the exploration stage.
- Also, anytime any changes are made to the code, regression testing is run.
- When necessary, attend or hold review sessions with developers and other teams.
- Maintain the software's quality.
How to become a Software Tester?
Here’s a step-by-step process to become a software tester for a rewarding career path:
1. Get Basic Computer Knowledge
To be a software tester, some basics about computer operation must be taught. The following includes operating systems, software applications, and using the internet. If new to the computer world, you should first gain some fundamental knowledge of Microsoft Windows or macOS and standard programs like Microsoft Office or Google Suite.
Read: End to End Testing Best Practices
2. Learn the fundamentals of Software Testing
Once you get a basic understanding of computers, you can start learning the foundations of software testing. To begin with, learn types of software testing like:
- Performance testing
- Functional testing`
- Usability testing
- Security testing
You should also focus on learning the basics of the software testing lifecycle, like test planning, test execution, test design, and test reporting.
3. Become familiar with different testing tools and techniques of software testing
You will work with various techniques and tools as a software tester. So, it's important to familiarise with popular testing tools like:
- Appium
- Selenium
- TestRail
- JIRA
4. Learn about their benefits, features, and limitations and understand the use of these tools to execute test cases, create cases, and report defects.
Techniques to be learned are:
- White box testing
- Black box testing
- Exploratory testing
- Grey box testing
Understand every technique's limitations and benefits and the process of applying them in different testing scenarios.
5. Gain knowledge of Programming Languages
It is unnecessary, but knowing programming languages and coding can benefit a software tester. Familiarise with Python, Java, JavaScript, and C# programming languages. Learn about semantics, syntax, and data types used for each language. Learn how to write simple programs, use version control systems, and debug code.
Mastering programming languages would help you understand the software development process and effectively communicate with developers.
Also Read: Data Manipulation Language
6. Earn Certification
Get certified to demonstrate your commitment and expertise in software testing. Earning certification in Software testing would help you learn the fundamentals of testing methodologies and various testing techniques. To further advance your career and get job opportunities as a software tester, certifications help by increasing the chances. There are different types of certification to acquire. Do your research and identify which ones suit you the best to pursue.
7. Understand SDLC
You will work closely with developers, stakeholders, and project managers as a software tester. Building Armstrong's software development life cycle knowledge, including Agile methodologies, Kanban, and Scrum framework, would contribute to the software development process. Learn about the different phases of the software development life cycle, including requirements gathering, design, development, testing, and deployment. Understand how to create test cases, execute tests, and report defects in each phase.
8. Develop a professional network
Networking is important in every field, even software testing. Connect with professionals in your field, join online communities and attend industry events. This will help you to stay updated on industry trends, best practices, and job opportunities. Join online forums and communities such as Reddit's r/software testing, Stack Overflow, and LinkedIn groups dedicated to software testing. Go to conferences, meet people, and attend webinars where you can learn from industry experts and meet other people.
9. Apply for jobs
The final step involves applying for permanent software testing jobs to become a software tester. Look at the job descriptions for every position, as their requirements may vary widely. You can easily find open software testing job openings on various online job and career platforms. Create or update your resume with your experiences, objectives, skills and achievements.
How to become a Software Tester with no experience?
Beginning a journey of a career in software development is an enjoyable experience. Generally, you can start your career in software development by following your passion and gaining the required skills. To help you out, we have made things simple and easy by breaking them down into practical steps. Follow the steps to convert your dreams into a successful career.
Improve your coding skills
To be a successful software developer, you must have solid coding skills. This can be done through regular practice, trying different programming languages and keeping up with the latest technologies. Make it a goal to code daily, even for a few minutes.
Create a portfolio
A portfolio is where you showcase your best work as a software developer. This can be in the form of a website, GitHub profile or a document. Your portfolio should contain a sample of your coding projects with a detailed overview of tools used, issues faced, and solutions used. This will allow prospective employers or clients to evaluate your skills and experiences.
Build your online presence
In the digital age, an online presence is necessary for every professional, especially software developers. Make a professional LinkedIn profile showcasing your skills, experience and achievements. You can even create a personal website or blog to share your views and opinions on programming, technology, and the industry.
Network with other programmers
Networking is a vital part of any career, including software development. You meet fellow programmers through a conference or a meetup to learn new technologies and share your experiences. Connect with other developers, get your questions answered, and receive feedback on your work by joining online communities such as GitHub, Stack Overflow, or Reddit's r/learn programming.
Earn certification
Certifications can benefit software developers as they demonstrate expertise in specific technologies or programming languages. Consider obtaining certifications like AWS Certified Developer, Google Cloud Certified - Professional Cloud Developer, or Oracle Certified Java Programmer. These certifications can help you stand out in a competitive job market and increase your earning potential.
Make a strong resume
A strong resume is essential for any job application, and software development is no exception. Tailor your resume to the job you're applying for, highlighting your relevant skills, experience, and achievements. Use clear and concise language, and proofread your resume multiple times for any errors or typos.
Build projects of your own
Lastly, creating projects is a great way to showcase your abilities and creativity as a software developer. Consider ideas for a project you might want to do, such as a mobile app, web app, or machine learning model, before designing, developing, and deploying it. Get feedback from other developers to improve your project. Post your project on GitHub or GitLab and be ready to discuss it with employers or clients.
Also Read: Is Software Testing is Good career?
How do you become a software tester without a degree?
Follow these steps to gain the essential skills and knowledge needed to start a career in software development, even without a degree.
Enroll in an online course
To get started, enroll in a comprehensive training program that teaches ethical hacking from the ground up. This is an incredible opportunity; its popularity is evident because over 508,000 individuals have already participated. The course includes 23 downloadable resources and spans 16 hours, providing a thorough education in this critical field. Upon completion, you'll receive a prestigious certification recognizing your expertise in ethical hacking.
Get into freelancing
As a strategic starting point, consider tackling smaller, low-pressure projects that allow you to ease into the workflow. You might even take on a few pro-bono projects to garner genuine client feedback, ultimately proving invaluable in shaping your professional trajectory.
Gain knowledge
While unnecessary, using extra resources to learn something helps you become a better software tester. Reading books, post blogs, etc., enables you to upgrade your knowledge and skills. It is vital to test software because of continuous advancement and change. To do well in this job, you must have a strong ability to learn by doing. This skill will help you and leave an impression on your clients! They will love that you are learning and growing. By continuously learning and improving, you can deal with testing software and have a promising career.
Prepare your resume
With your skills honed and experience gained, it's time to showcase your credentials to potential employers. Craft a compelling CV highlighting your strengths, achievements, and relevant experience. If needed, consider seeking guidance from a career counsellor or mentor to help create a standout resume.
Once you have a solid CV, you can confidently begin your job search. By following the steps outlined earlier and possessing a well-crafted resume, you'll be well-positioned to land your first job in software testing. Your hard work and dedication will pay off, and you can look forward to launching a successful and rewarding career.
Software Tester Qualifications and Skills:
Becoming a proficient software tester requires a combination of technical knowledge, analytical skills, and attention to detail. While educational backgrounds and certifications can vary, there are certain qualifications explained, that are generally sought after in the industry:
Educational Background: A bachelor's degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field is often considered a strong foundation for a software testing career. However, for StarAgile’s Automation Testing, everyone, even freshers, are welcome. Software testing is a good career choice, offering excellent growth opportunities and a chance to work with cutting-edge technologies.This educational background provides the necessary theoretical understanding of software development principles and concepts.
Technical Proficiency: A software tester should have a solid grasp of programming languages, database management systems, and testing tools. Proficiency in languages like Java, Python, or C# allows testers to comprehend code structures and write effective test scripts.
Testing Methodologies: Familiarity with various Software testing tools and testing methodologies, such as manual testing, automated testing, and exploratory testing, is crucial. In the realm of automation and continuous delivery, Docker in DevOps plays a significant role in containerizing applications for testing and integration purposes. Each methodology has its own strengths and weaknesses, and a skilled tester knows when and how to apply them appropriately.
Problem-Solving Skills: Software testers need to be adept at identifying, isolating, and reproducing defects. Strong problem-solving skills enable testers to work collaboratively with developers to resolve issues effectively.
Attention to Detail: Meticulous attention to detail is paramount in software testing. Testers must meticulously follow test plans, document test cases, and provide accurate reports on defects and their impact.
Communication Skills: Effective communication is essential for conveying testing results, collaborating with development teams, and contributing to the improvement of software quality. Clear and concise communication ensures that the testing process is aligned with project goals.
Now we know what these qualifications are, so let’s have a look what makes a software tester
Read More: Software Testing Techniques
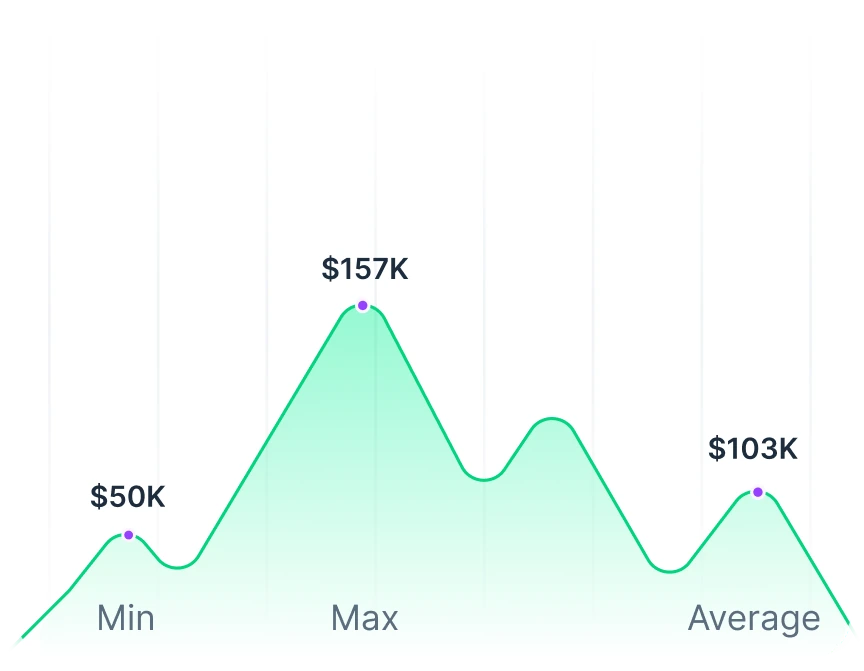
Software Tester Salary
IT
Software testing originated in the IT and technology sector, and it remains one of the most lucrative industries for testers. On average, software testers in this sector can earn between $85,000 and $120,000 annually, depending on location, experience, and specific company.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry is another significant sector that employs software testers to ensure the quality and safety of medical software applications. Testers in this industry can earn between $80,000 to $120,000 per year.
Finance and Banking
Software applications are put to use in the finance and banking industry to facilitate transactions, track investments, and manage customer records. Software testers in this industry are paid well, with average salaries falling between $90,000 and $140,000 annually.
E-commerce
E-commerce companies use software applications to manage online transactions, inventory, and customer relationships. Software testers in this sector can earn average salaries ranging from $70,000 to $110,000 annually.
Also Read:Manual Testing vs Automation Testing
FAQs
1. What skills do I need to become a software tester?
Becoming a software tester requires a unique blend of skills. You'll need some basic programming knowledge, like Java or Python. However, you'll also need to understand how software development works, including Agile and Scrum methodologies. And let's not forget about testing frameworks and tools - Selenium and JUnit are essentials. Of course, you'll also need top-notch analytical and problem-solving skills, attention to detail and excellent communication skills.
2. What kind of experience does one need to start with software testing?
Diving into software testing might feel overwhelming at first, but trust me, it’s not as complicated as it seems. Start by getting a good grasp of the fundamentals of programming and software development. Once you have that down, take some time to explore different testing frameworks and tools. A great way to sharpen your skills is by practising on open-source projects or even your projects. Don’t forget to join online communities and forums to connect with fellow testers and soak up their insights. And don’t hesitate to go for internships or entry-level jobs to kickstart your career!
3. Explain the difference between automated and manual testing.
Manual testing is what it sounds like - testing software by hand without using any automated tools. This is usually how we do exploratory, usability, and user acceptance tests. On the other hand, automated testing uses software tools to run tests, saving a ton of time and effort. We usually use automated testing for regression, unit, and integration testing.
4. How can a software tester stay updated with new trends and technologies?
Staying current in software testing requires some effort, but it's doable. I recommend attending conferences, meetups, and webinars to learn from industry experts. Joining online communities and forums is also a great way to connect with other testers and learn about new tools and techniques. And, of course, reading industry blogs and publications is a great way to stay informed. Don't forget to take online classes or certification programs to boost your skills!
5. Is it possible to work remotely as a software tester?
You can do software testing from the comfort of your own home! A lot of companies are open to remote work these days. Sure, some projects might need you to be on-site, especially if they involve sensitive or confidential information. But as long as you have a solid internet connection and the right tools, you can handle software testing from just about anywhere!







 Software testing has quickly become a pivotal discipline within today's fast-evolving technological environment, serving to ensure the delivery of top-quality, user-friendly applications that satisfy customer demands while remaining cost competitive.
Software testing has quickly become a pivotal discipline within today's fast-evolving technological environment, serving to ensure the delivery of top-quality, user-friendly applications that satisfy customer demands while remaining cost competitive.